What is Particulate Matter?
Another pollutant of concern in Central Texas is particulate matter (PM) or particle pollution. PM pollution causes the majority of days when air pollution is considered "not good" in the region. While PM levels rarely become high enough to affect sensitive groups, people who are especially sensitive to air pollution can be affected.
What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution): the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye. Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope.
Particle pollution includes:
- PM10 : inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometers and smaller
- PM2.5 : fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
- How small is 2.5 micrometers? Think about a single hair from your head. The average human hair is about 70 micrometers in diameter – making it 30 times larger than the largest fine particle.
PM2.5 is the particle pollution size that is of concern in Central Texas!
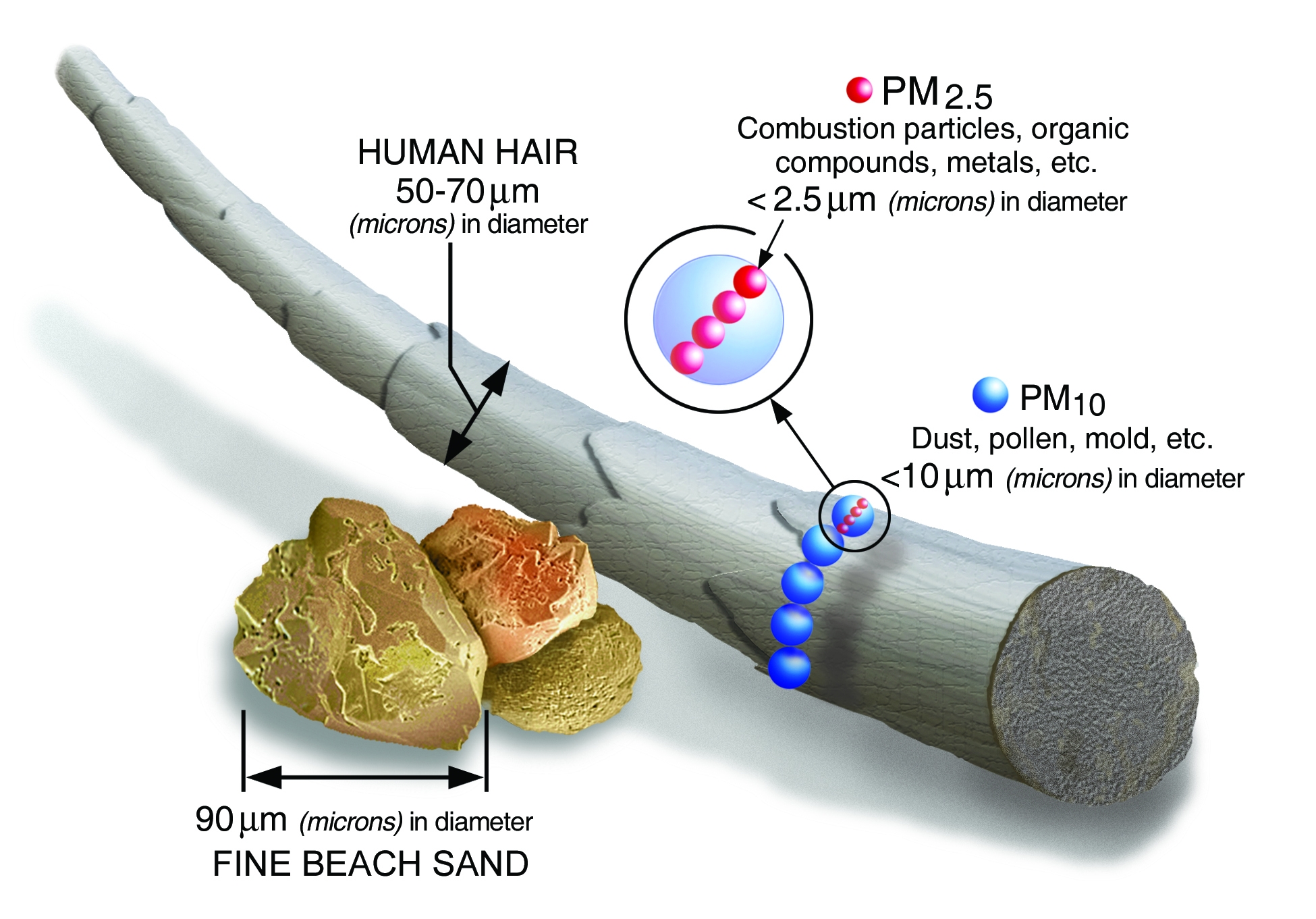
Source - https://www.epa.gov/pm-polluti...
What are the sources of PM?
These particles come in many sizes and shapes and can be made up of hundreds of different chemicals.
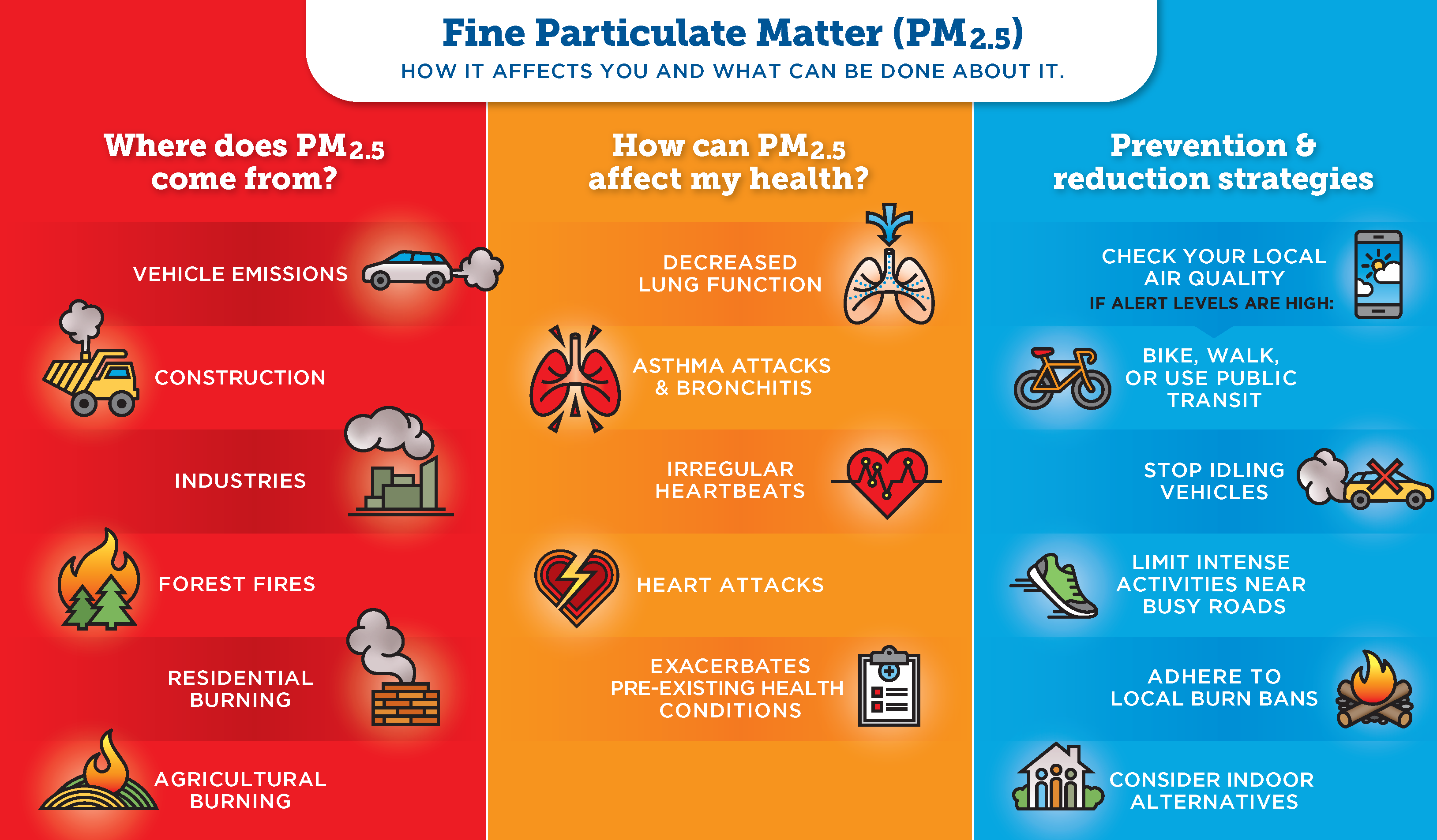
Some are emitted directly from a source, such as construction sites, unpaved roads, agriculture, mines and quarries, smokestacks or fires.
Most particles form in the atmosphere as a result of complex reactions of chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are pollutants emitted from power plants, industries, and automobiles.
What are the Health Effects of PM?
PM contains microscopic solids or liquid droplets that are so small that they can be inhaled and cause serious health problems. PM2.5 can pose the greatest risk to health because PM2.5 can get deep into your lungs and even into your bloodstream.
PM is linked to a number of health problems:
- Increased respiratory symptoms, such as irritation of the airways, coughing or difficulty breathing
- Aggravated asthma
- Decreased lung function
- Nonfatal heart attacks
- Irregular heartbeat
- Irritation of the nose, throat, and eyes.
- Premature death in people with heart or lung disease
Some people are more sensitive to PM than others. Sensitive groups include children, older adults, people with lung or cardiovascular disease, and even healthy adults, who are active outdoors, can experience PM's harmful effects.
How does PM affect the environment?
Visibility Impairment
PM2.5 is the main cause of reduced visibility (haze) in parts of the United States, including many of our treasured national parks and wilderness areas.
Environmental damage
Particles can be carried over long distances by wind and then settle on the ground or water. Depending on their chemical composition, the effects of this settling may include:
- making lakes and streams acidic
- changing the nutrient balance in coastal waters and large river basins
- depleting the nutrients in soil
- damaging sensitive forests and farm crops
- affecting the diversity of ecosystems
- contributing to acid rain effects.

When does Central Texas typically experience high PM?
Unlike ozone, high PM can happen at any time of the year. You may visibly notice high PM during the summer when the dust from the Saharan Desert travels across the Atlantic to Central Texas, usually in June or July. Wildfires and smoke will generate PM pollution, too. It is important to "Be Air Aware" and check the Air Quality Index regularly if you're in a sensitive group for PM.